Virtual Reality in Medical Education: Immersive Learning Experiences
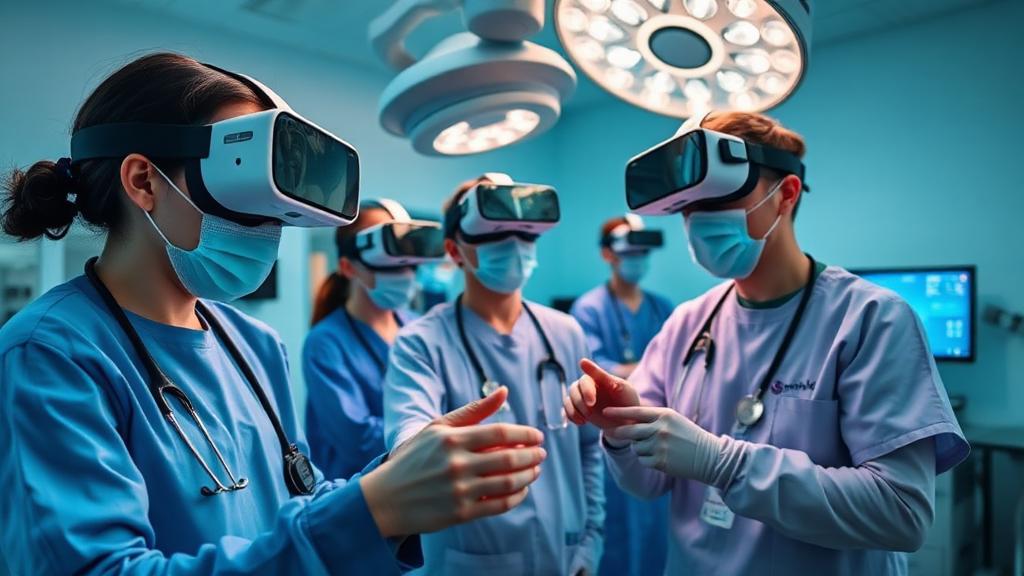
Virtual Reality is transforming medical education from a primarily theoretical discipline into an immersive, hands-on experience. As VR technology becomes more accessible and sophisticated, it's creating unprecedented opportunities for safe, repeatable, and highly effective clinical training.
The VR Revolution in Healthcare Education
Traditional medical education has long struggled with the challenge of providing sufficient hands-on experience without compromising patient safety. Virtual Reality addresses this fundamental limitation by creating realistic, risk-free environments where healthcare professionals can practice complex procedures, make mistakes, and learn from them without real-world consequences.
In the GCC region, where healthcare systems are rapidly modernizing and expanding, VR medical education offers a scalable solution for training the growing healthcare workforce while maintaining the highest standards of clinical competency.
Applications of VR in Medical Training
1. Surgical Simulation
VR surgical simulators provide incredibly detailed training environments:
- Haptic feedback that mimics the feel of real surgical instruments
- Anatomical accuracy based on real patient imaging data
- Procedural variation allowing practice of different case scenarios
- Performance tracking with detailed analytics and feedback
- Collaborative training enabling multi-user surgical team practice
2. Clinical Diagnosis Training
VR creates immersive patient interaction scenarios:
- Virtual patients with realistic symptoms and responses
- Diagnostic challenges across various medical specialties
- Decision-making trees that adapt to trainee choices
- Cultural diversity in patient presentations and communication styles
Advantages of VR-Based Learning
Safe Learning Environment
VR eliminates the risk associated with learning on real patients while maintaining educational effectiveness:
- No patient safety concerns during skill acquisition
- Unlimited practice opportunities without resource constraints
- Ability to simulate rare or dangerous conditions safely
- Stress-free environment for building confidence
Personalized Learning Pathways
VR systems can adapt to individual learning needs and progress:
- Adaptive difficulty that adjusts to skill level
- Personalized feedback based on individual performance patterns
- Learning analytics that identify areas for improvement
- Self-paced progression allowing learners to advance when ready
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Technology Infrastructure
Successful VR implementation requires careful consideration of technical requirements:
- Hardware specifications for optimal performance and user experience
- Network capacity for multi-user and cloud-based applications
- Content management systems for educational material organization
- Maintenance protocols to ensure consistent equipment functionality
Content Development
Creating effective VR educational content requires specialized expertise:
- Collaboration between medical experts and VR developers
- Evidence-based curriculum design adapted for immersive environments
- Regular content updates to reflect evolving medical practices
- Cultural adaptation for regional healthcare contexts
"Virtual Reality doesn't replace traditional medical education—it enhances it by providing experiences that were previously impossible, allowing learners to practice complex procedures and scenarios in a safe, controlled environment."
Integration with Traditional Learning
Blended Learning Approaches
The most effective VR implementations combine virtual and traditional learning methods:
- Theory foundation through traditional lectures and reading
- VR practice for hands-on skill development
- Real-world application under supervision
- Peer discussion and case study analysis
Assessment and Certification
VR enables new approaches to competency assessment:
- Objective performance metrics collected automatically
- Standardized scenarios for consistent evaluation
- Continuous assessment throughout the learning process
- Portfolio-based evidence of competency development
Specialty-Specific Applications
Emergency Medicine
VR excels in emergency scenario training:
- High-pressure situation simulation without risk
- Team-based emergency response training
- Rare emergency condition exposure
- Communication skills in crisis situations
Pediatric Medicine
Special considerations for pediatric VR training:
- Age-appropriate virtual patient models
- Parent interaction scenarios
- Pediatric-specific procedures and considerations
- Child communication and comfort techniques
Measuring VR Learning Effectiveness
Learning Outcomes Assessment
VR systems provide rich data for evaluating educational effectiveness:
- Skill acquisition metrics tracking improvement over time
- Knowledge retention testing compared to traditional methods
- Transfer to real practice evaluation in clinical settings
- Learner satisfaction and engagement measurements
The Future of VR in Medical Education
As VR technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated applications:
- AI-powered patients with dynamic responses and learning capabilities
- Augmented reality integration blending virtual and real environments
- Remote collaboration enabling global learning communities
- Personalized avatars representing diverse patient populations
Implementation Recommendations
For institutions considering VR adoption:
- Start with pilot programs to demonstrate value and refine approaches
- Invest in faculty training to ensure effective integration
- Develop partnerships with VR content creators and technology providers
- Plan for scalability as technology becomes more accessible
Virtual Reality represents a fundamental shift in how we approach medical education—one that promises safer training, better outcomes, and more engaged learners. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, VR will become an essential tool in developing the next generation of healthcare professionals.

Dr. Tabian Hassan
CME Director
Dr. Tabian Hassan leads continuing medical education initiatives at MME Group, specializing in innovative educational technologies and immersive learning experiences. Her expertise in VR medical education helps healthcare institutions implement cutting-edge training solutions that improve learning outcomes and clinical competency.